
Titanium
Titanium is a metal with a high corrosion resistance. It quickly forms a stable surface layer (titanium oxide) with similar characteristics such as ceramics. It also prevents a dissolving of the metal. Veneering is possible.
In recent years, the use of the material titanium has taken an unexpected upturn.
Price increases in the Pd (Palladium)-and Au (Gold)alloys, as well as the increasing of allergies are certainly a reason for the increased interest in the new-old material titanium.
If a dentistry wants to successfully master this material, it must invest money ... a lot of money, ideas ... many ideas and perseverance... endless endurance:)
Titanium is difficult to handle! It is very hard, we can not veneer, it does not always fit exactly, it is too expensive - and titanium processing needs to be learned - from technicians as well as the dentist.
With a good know-how: Titanium can be easy to work with!
The fitting is similar to gold, ceramic bindings have aesthetic quality, and you can clip it to most dental models of all divisions.
Delivery / Products
Wieland:
Titanium Blank
Dentaurum:
Pure titanium tritan
Gold
It is used for galvanic plastics, dental crown scaffolds, and secondary telescopic crowns. It is possible to veneer it, as long as a ceramic mass in tooth-colored structures is used. The stability of it is not as high as the cast frames (metal ceramic).
Gold alloys
Gold alloys are normally subdivide in high-containing- or reduced gold alloys. Besides, so-called -poor-gold alloys- are existing as well.
However, high-containing gold alloys have perfect processing properties and a high corrosion resistance. Veneering (metallic ceramic) is easily possible. Consequently, this type of gold alloy is favored.
A gold alloy with copper is also known as a red-, a gold alloy with silver is known as a white-, and a mixture with both metals is also called a mixed alloy.
Used for
Fixed Prosthesis (dental crowns, bridges), root pins, prosthetic implantology and auxiliary parts
Palladium Alloy
Palladium is an expensive material. It is usually used with silver- or gold alloys.
Used for Fixed Prosthesis (crowns, bridges), or in use with ceramics
» Zircon
» Noble metals
» NEM-alloys
» Dental Resins
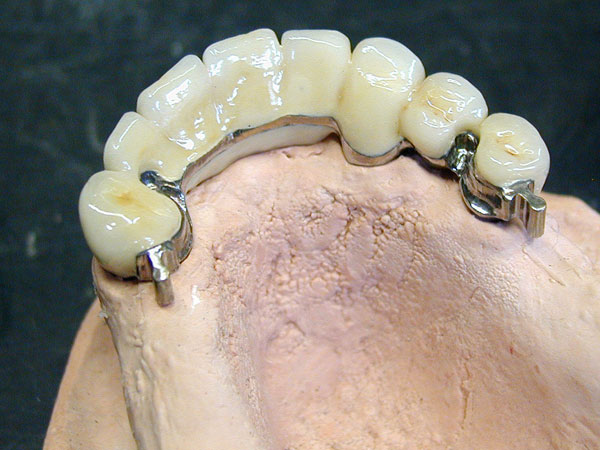
The benefits of using titanium:
- Biocompatibility
- Corrosion stability
- No potential equalisation / No uncontrollable ion releas
- Tasteless
- High efficiency
- Low thermal irritations of hard and soft tissues by low thermal conductivity
- Universal applicability
- High mechanical strength, low weight
- Mono material in a practical purity of 99.8% Ti
- Resists high differences of temperature, veneering with ceramics is possible
- The use of laser welding technology increases the advantage of the mono material titanium
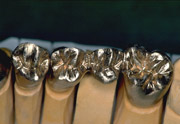
- Fine gold (99,9 m% gold)
- Galvano gold (99,8 m% gold)
Supplier / Products
Goldquadrat:
Bio Keramik G, Universalgold P SiPal alloys, Palladiumgold 52,
Palladiumgold 6, Inlaygold T, special ceramic Universalgold PDF
Wieland:
Porta Geo, Porta Geo Ti, Porta Reflex, Porta Implantat, Simidur S 1 S, Spargold
Auropal KF, Portadur IN, Galvano AGC Wieland, Silver alloy Simidur A
Koos:
Auronorm
Degudent:
Degunorm
M + K Jena:
Jena pall M



